How Async/Await Really Works in C# 🔗
Very detailed history of async programming in C#, which has always been hard to get right. This describes the problems, the solutions, and everything in between.
How to start using .NET Background Services 🔗
I'm not sure if this is new to me, but I'll keep this here as a reference. To run a background service in .Net:
In Program.cs:
services.AddHostedService<Worker>();Where Worker is a class that extends BackgroundService. The core method is ExecuteAsync, and there are also lifecycle event methods StartAsync and StopAsync.
Feature toggle management in .NET Core 🔗
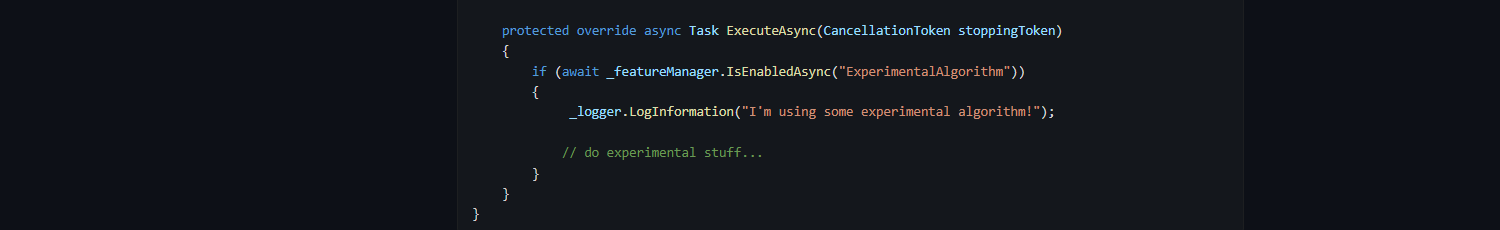
Neatly following on from that is .Net's feature management package. They demo it with a Worker, although that's just a coincidence that I happened to read this article after the one above:
var host = Host.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.ConfigureServices(services =>
{
services.AddHostedService<Worker>();
services.AddFeatureManagement();
})
.Build();
public class Worker : BackgroundService
{
private readonly ILogger<Worker> _logger;
private readonly IFeatureManager _featureManager;
public Worker(ILogger<Worker> logger,
IFeatureManager featureManager)
{
_logger = logger;
_featureManager = featureManager;
}
protected override async Task ExecuteAsync(CancellationToken stoppingToken)
{
if (await _featureManager.IsEnabledAsync("ExperimentalAlgorithm"))
{
_logger.LogInformation("I'm using some experimental algorithm!");
// do experimental stuff...
}
}
}As well as calling _featureManager.IsEnabledAsync directly, you can also add it as an attribute on Asp.Net Core controllers:
[FeatureGate(FeatureFlags.ExperimentalAlgorithm)]
public class ExperimentalController()
{
// ...
}And there's lot more configuration and usage possibilities.
Refactor your .NET HTTP Clients to Typed HTTP Clients 🔗
This article explains about using IHttpClientFactory and typed clients instead of new HttpClient(), which I assume you already know by now, but it goes on to describe in detail how you should really use named/typed clients.
6 useful extensions for IEnumerable 🔗
Exactly what it says:
var isEmpty = numbers.Empty<int>().IsNullOrEmpty();
var (even, odd) = numbers.Partition(n => n % 2 == 0);
var median = numbers.Median();
var mode = numbers.Mode();
var standardDeviation = numbers.StandardDeviation();
var random = numbers.Shuffle();How to detect Globalization-Invariant mode in .NET 🔗
I wish I'd known earlier that Globalization-Invariant mode was a thing. I assume it means that instead of writing Invariant("blah") all the time in the code, you can set an environment variable DOTNET_SYSTEM_GLOBALIZATION_INVARIANT to true.
Six ways to shoot yourself in the foot with healthchecks 🔗
Health checks are nice, but don't let them cascade into disaster.
Where are Objects Allocated in C#? Understanding Heap and Stack 🔗
Understanding the difference between the heap and the stack, and how to change it (ref, in, out keywords).